Results: Generation + Tracking
(Generation only & stylization: coming soon.)
Summary
Robo-Saber is the first motion generation system for playtesting virtual reality (VR) games. Given in-game object configurations—colored notes, bomb notes, and obstacles in Beat Saber—Robo-Saber generates three-point (3p) trajectories for the VR headset and two handheld controllers, guided by short style reference gameplay examples (contextual exemplars) from the same player. We train on the large-scale BOXRR-23 dataset paired with map files from BeatSaver, producing a style-conditioned model that captures diverse skill levels and movement patterns across the player population.
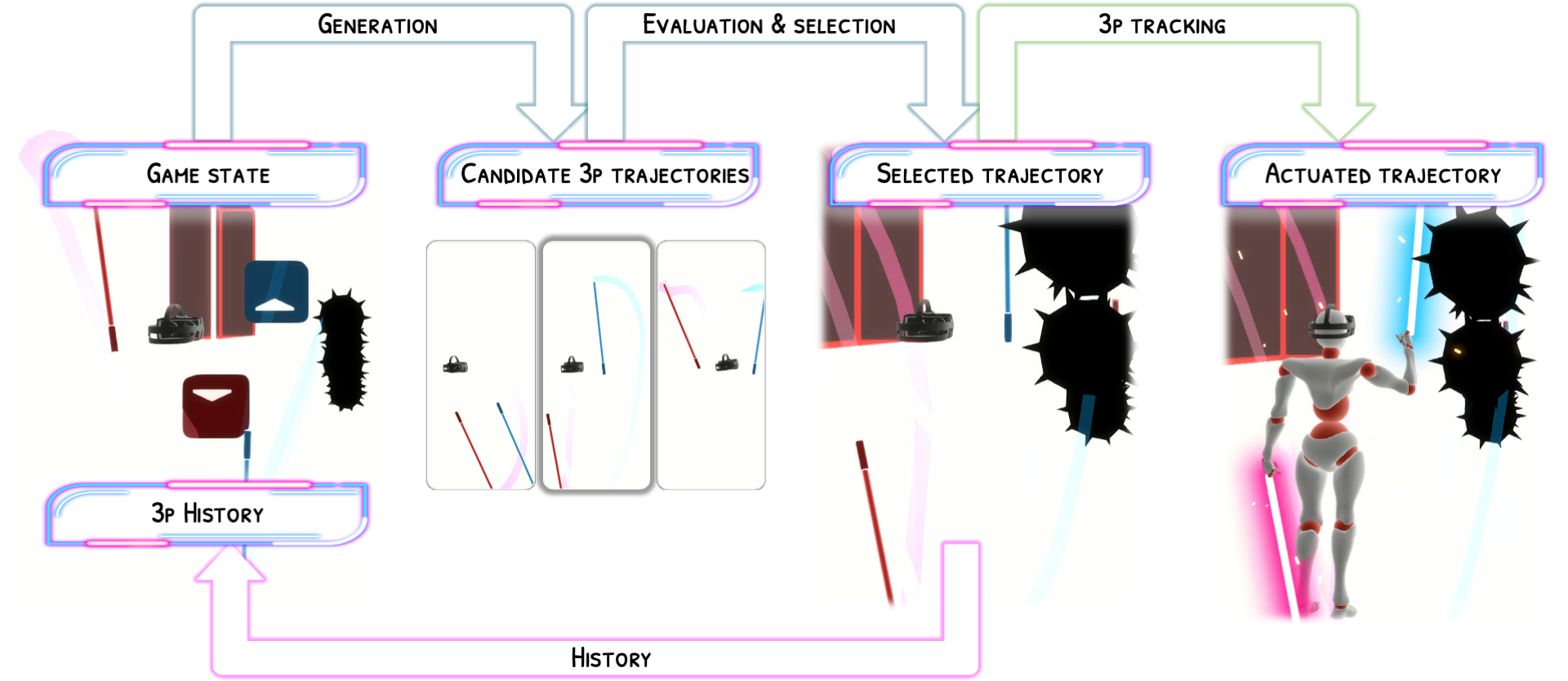
Robo-Saber follows a generate–simulate–select pipeline. A reference-conditioned generative model samples multiple candidate 3p trajectories. Each candidate is then evaluated using TorchSaber, a custom GPU-accelerated Beat Saber simulator we develop. The highest-scoring trajectory is selected and fed back autoregressively, producing minutes-long gameplay sequences on entirely new maps. The generated 3p trajectories can optionally drive a physics-based full-body tracking controller (PHC, Luo et al., 2023), fine-tuned on custom Beat Saber motion capture data, for whole-body gameplay simulation.
Our training data comprises millions of gameplay sequences accumulated from over 70k players in BOXRR-23, aligned with map files from BeatSaver. Naturally, different players move differently in terms of how and how well they can play.
|
|
We formulate generative motion planning as a simple supervised learning problem: given the in-game object arrangements and the headset/handheld controller state (left), we task our model with predicting the 1-second future trajectory (right).
However, the key question remains: how should we represent the individual players’ variability in gameplay styles?
Our idea is to use short sample clips of actual gameplay (we dub “contextual exemplars”) to represent individual players’ gameplay skills and movement patterns. For example, a skilled expert player’s contextual exemplars (left) show confident and aggressive swings, while a novice player’s (right) shows cautious and small swings.
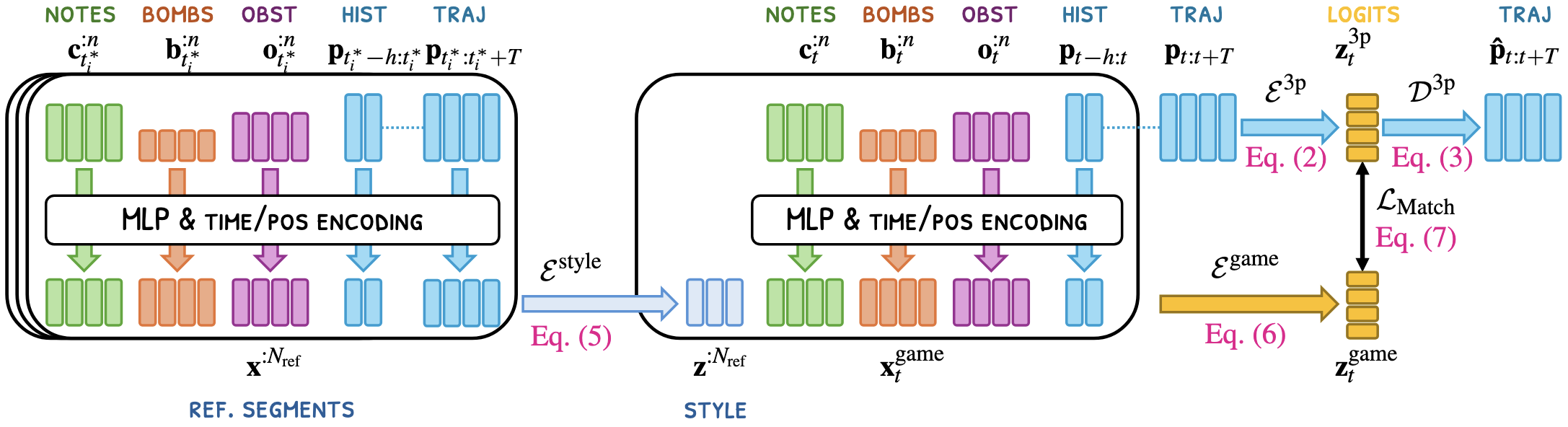
Our generative model extends Categorical Codebook Matching (CCM, Starke et al., 2024) with two key contributions. First, we introduce a Transformer-based style encoder that embeds contextual exemplars into a style conditioning signal, added alongside a Transformer-based game encoder that predicts the latent categorical distribution for the next 3p motion chunk from the game state and pose history. Second, we replace CCM’s MSE-based matching loss with a Jensen-Shannon divergence (JSD) loss for a more principled alignment between the Gumbel-Softmax VAE’s encoding of the target motion and the game encoder’s prediction.
By feeding the contextual exemplars along with in-game object arrangements and player model state to the model, we can produce output consistent with the target skill level and movement output. The generated trajectory (right) reflects the confident and fast swings of the exemplars (left).
Similarly, the model can produce novice-like movements by feeding a novice player’s contextual exemplars.
The resulting model achieves elite-level Beat Saber gameplay and, by conditioning on a few reference segments, correlates strongly with individual players’ scores on held-out maps (r = 0.789), enabling personalized score prediction for brand-new content.
Cite Us
@inproceedings{kim2026robo,
title={Robo-Saber: Generating and Simulating Virtual Reality Players},
author={Kim, Nam Hee and Liu, Jingjing May and Lehtinen, Jaakko and H{\"a}m{\"a}l{\"a}inen, Perttu and O'Brien, James and Peng, Xue Bin}, booktitle={arXiv preprint},
pages={1--10},
year={2025}
}
